CBSE Board Syllabus – Geography Class 12
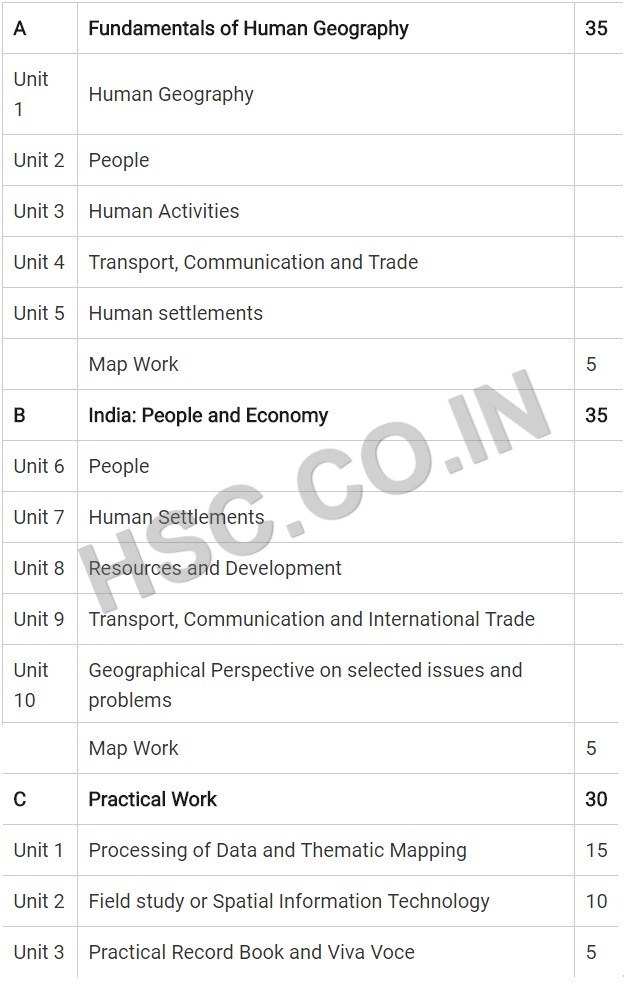
A. Fundamentals of Human Geography
Unit 1: Human Geography:
- Nature and Scope
Unit 2: People
- Population-distribution,density and growth
- Population change-spatial patterns and structure; determinants of population change;
- Age-sex ratio; rural-urban composition;
- Human development – concept; selected indicators, international comparisons
Unit 3: Human Activities
- Primary activities – concept and changing trends; gathering, pastoral, mining, subsistence agriculture, modern agriculture; people engaged in agricultural and allied activities – some examples from selected countries.
- Secondary activities-concept; manufacturing: types – household, small scale, large scale; agro based and mineral based industries; people engaged in secondary activities – some examples from selected countries.
- Tertiary activities-concept; trade, transport and tourism; services; people engaged in tertiary activities – some examples from selected countries.
- Quatenary activities – concept; people engaged in quatenary activities – case study from selected countries.
Unit 4: Transport, Communication & Trade
- Land transport – roads, railways; trans-continental railways.
- Water transport – inland waterways; major ocean routes.
- Air transport – Intercontinental air routes.
- Oil and gas pipelines.
- Satellite communication and cyber space- Importance and usage for geographical information; use of GPS.
- International trade-Bases and changing patterns; ports as gateways of international trade, role of WTO in International trade.
- Ocean: National rights and international treaties.
Unit 5: Human settlements
Settlement types – rural and urban; morphology of cities (case study); distribution of mega cities; problems of human settlements in developing countries.
Map Work
Map Work on identification of features based on 1-5 units on the outline/Physical/Political map of World.
B. India: People and Economy
Unit 6: People
- Population: distribution, density and growth; composition of population – linguistic, religious; sex, rural-urban and occupational-regional variations in growth of population.
- Migration: international, national-causes and consequences.
- Human development: selected indicators and regional patterns.
- Population, environment and development.
Unit 7: Human Settlements
- Rural settlements – types and distribution.
- Urban settlements – types, distribution and functional classification.
Unit 8: Resources and Development
- Land resources – general land use; agricultural land use, Geographical conditions and distribution of major crops (Wheat, Rice, Tea, Coffee, Cotton, Jute, Sugarcane and Rubber), agricultural development and problems.
- Water resources – availability and utilization-irrigation, domestic, industrial and other uses; scarcity of water and conservation methods -rain water harvesting and watershed management.
- Mineral and energy resources – distribution of metallic (Iron ore, Copper, Bauxite, Manganese); non-metallic (Mica, Salt) minerals; conventional (Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas and Hydroelectricity) and non-conventional energy sources (solar, wind, biogas) and conservation.
- Industries – types, factors of industrial location; distribution and changing pattern of selected industries-iron and steel, cotton textiles, sugar, petrochemicals, and knowledge based industries; impact of liberalization, privatisation and globalisation on industrial location; industrial clusters.
- Planning in India – target group area planning (case study); idea of sustainable development (case study).
Unit 9: Transport, Communication and International Trade
- Transport and communication-roads, railways, waterways and airways: oil and gas pipelines; Geographical information and communication networks.
- International trade – changing pattern of India’s foreign trade; sea ports and their hinterland and airports.
Unit 10: Geographical Perspective on selected issues and problems
- Environmental pollution; urban – waste disposal.
- Urbanisation, rural-urban migration; problems of slums.
- Land degradation.
Map Work
- Map work on locating and labelling of features based on above units on outline map of India.